Test images and datasets
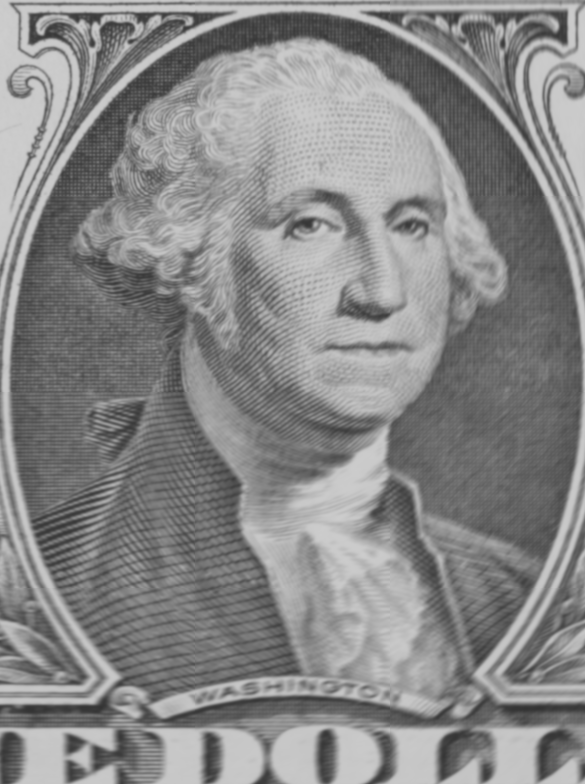
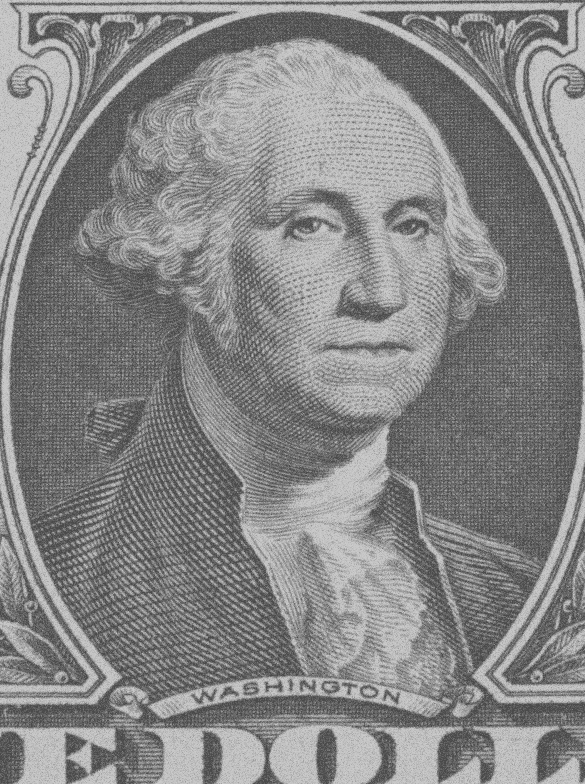
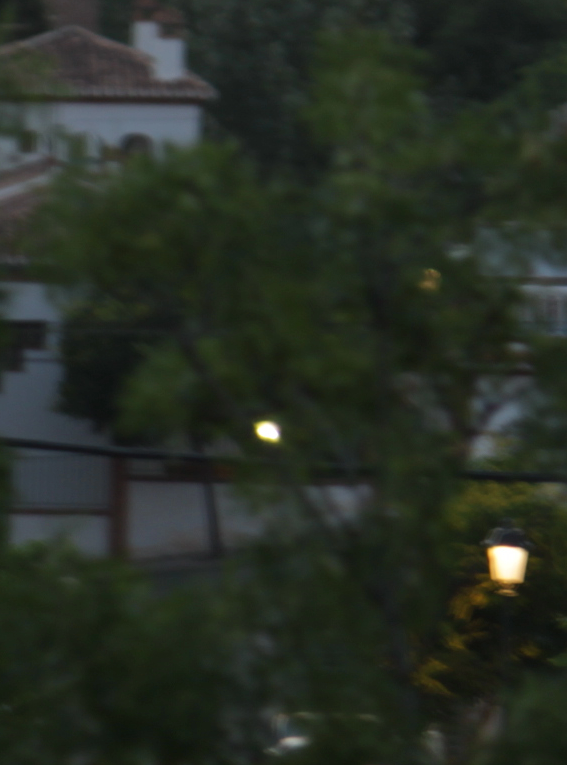
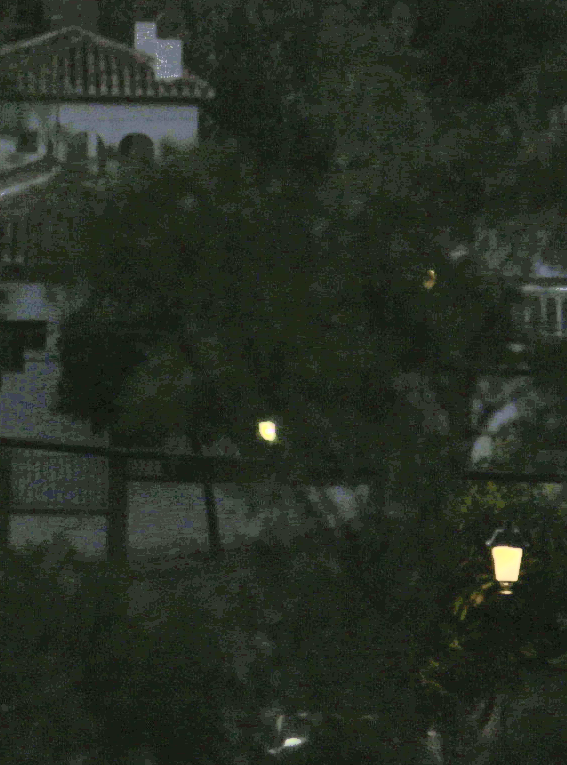
Dual exposure problem
We aim at recovering a sharp image in low light conditions by combining information from images with different exposure time. In particular, we will demonstrate that a pair of images, consisting of a correctly exposed but blurred image and a sharp but very noisy image due to the short exposure time, is enough to recover a free of blurring and noise image by combining the information of the pair of images.
The datasets used in the papers [1] and [2] are available for download here:
Please refer to the following papers if you use this data:
- M. Tallón, J. Mateos, S.D. Babacan, R. Molina, and A. K. Katsaggelos, “Space-variant blur deconvolution and denoising in the dual exposure problem”, Information Fusion, 2013. (Accepted for publication)
- M. Tallón, J. Mateos , R. Molina, and A.K. Katsaggelos, “Image prior combination in space-variant blur deconvolution for the dual exposure problem” in 7th International Symposium on Image and Signal Processing and Analysis (ISPA 2011), 408-413, Dubrovnik (Croatia), September 2011.
For more information, please visit the project page
Light field acquisition from blurred observations using a programmable coded aperture camera
We deal with the problem of acquiring a scene light field using a programmable coded aperture camera when the angular observations are out-of-focus. To capture the images we used the portable programmable coded aperture prototype that can be attached to any DSLR camera lens. We proposed a blind deconvolution method to deblur light fields.
Synthetic data
Simulating a 7x7 coded aperture array. Each image is taken assuming that only a single aperture is open, thus the dataset contains 49 images. Each aperture is simulated by a pin-hole camera positioned at the aperture position. The dataset contains, also, the real depth for each pixel of the image and the spatial position of the apertures.
Real data
Captured using the prototype with a 3x3 coded aperture array. Each image is taken by opening only a single aperture. The set has 9 images numbered 1 to 9
real data, single aperture dataset
Also, a set of 9 images was captured using multiplexed coded apertures. Each image was captured with a ¡n aperture that has 5 open holes. The dataset includes the used masks and a picture with all the holes open (white frame) and another with all the holes closed (dark frame) for calibration.
real data, coded aperture dataset
Please refer to the following papers if you use this data:
- S.D. Babacan, R. Ansorge, M. Luessi, P. Ruiz, R. Molina, and A. K. Katsaggelos, “Compressive Light Field Sensing”, IEEE Transaction on Image Processing, vol. 21, no. 12, 4746-4757, December 2012.
- P. Ruiz, J. Mateos, C. Cárdenas, S. Nakajima, R. Molina, A.K. Katsaggelos, and CP team, “Light field acquisition from blurred observations using a programmable coded aperture camera” in 21th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO 2013), Marrakech (Morocco), September 2013. (Accepted for publication).
Depth map upsampling
The recent development of low-cost and fast time-of-flight cameras enabled measuring depth information at video frame rates. Although these cameras provide invaluable information for many 3D applications, their imaging capabilities are very limited both in terms of resolution and noise level. We developed a novel method for obtaining high resolution depth maps from low resolution depth maps and the corresponding high resolution color images.
The used datasets can be downloaded from here
Please refer to the following paper if you use this data:
- M. Tallón, S.D. Babacan, J. Mateos, M.N. Do, R. Molina, and A.K. Katsaggelos, “Upsampling and Denoising of Depth Maps via Joint-Segmentation” in European Signal Processing Conference, 245-249, Bucharest (Romania), August 2012.
For more information, please visit the project page